In today’s fast-paced, data-driven world, real-time mapping has emerged as one of the most powerful trends in Geographic Information Systems (GIS). By enabling instant access to location-based data as it’s collected, real-time GIS empowers surveyors, planners, developers, and governments to make quicker, smarter, and more informed decisions.
What Is Real-Time Mapping?
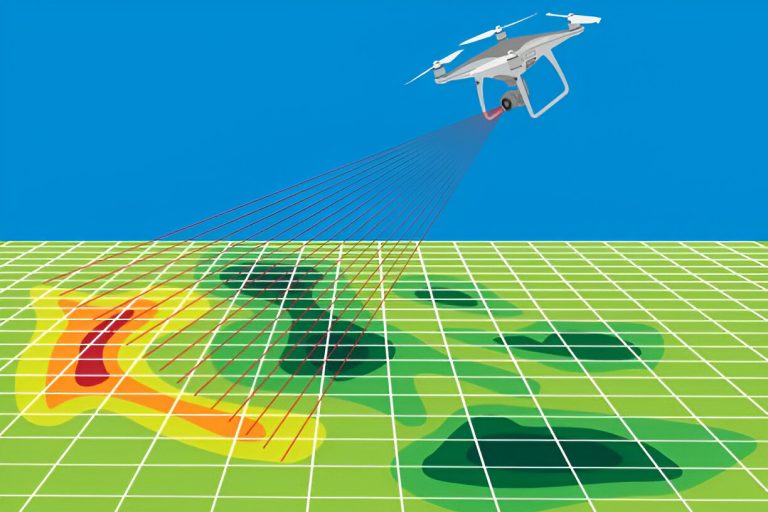
Real-time mapping refers to the continuous collection, transmission, and visualization of spatial data as events unfold. Unlike traditional GIS methods, which rely on post-processed data, real-time mapping delivers up-to-the-minute insights using sensors, mobile devices, GPS technology, and IoT (Internet of Things) integrations.
Example: A construction team can monitor the precise placement of foundations and underground utilities live on-site using real-time positioning data.
Key Benefits of Real-Time Mapping
Faster Decision-Making
Access to live spatial data allows professionals to respond immediately to changes in site conditions or environmental risks.Improved Accuracy
Continuous updates reduce the risk of working with outdated or incorrect data, which is especially critical in surveying and engineering.Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud-based platforms allow field teams and office-based professionals to view and act on the same live map from different locations.Proactive Risk Management
Real-time monitoring supports early detection of issues such as flooding, encroachment, or construction deviations.
Applications Across Industries
Land Surveying & Construction
Surveyors use GNSS-enabled tools to mark boundaries and align structures with pinpoint precision in real time.Infrastructure Development
Project managers track site activity, material movement, and equipment use live from dashboards.Environmental Monitoring
Sensors detect and map pollution, rainfall, or deforestation events as they occur.Disaster Response
Emergency teams access live spatial data to plan evacuation routes and coordinate relief efforts.
Technologies Enabling Real-Time Mapping
GNSS and RTK GPS for centimeter-level positioning
Mobile GIS apps like ArcGIS Field Maps or Survey123
IoT devices and environmental sensors
Drones with live-stream capabilities
Cloud GIS platforms for instant data sharing
Challenges to Consider
While real-time GIS offers numerous benefits, it also demands:
Reliable internet and network connectivity
High-capacity data storage solutions
Trained personnel for data interpretation
Investment in compatible hardware and software
Conclusion
Real-time mapping is redefining how spatial data is used in planning, surveying, and environmental management. As the demand for immediate insights grows, integrating real-time GIS tools will be essential for staying competitive, compliant, and future-ready in the land development space.